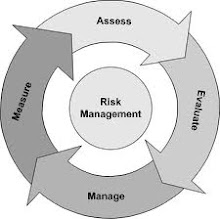
Dilemmas with ISO 27001 & BS 25999-2 internal auditors
- The management should view the internal audit as one of the best tools to improve the system, not only as a means to get certified.
- The internal auditor should be qualified – this means he/she must have experience in information security, information technology and auditing techniques. It does not mean that the auditor must be an expert in those fields.
- The internal audit should be performed in a positive way – the aim should be to improve your system, not to blame the employees for their mistakes.
ONE RESPONSE TO “DILEMMAS WITH ISO 27001 & BS 25999-2 INTERNAL AUDITORS”
Source
More
How to get ISO 27001 certification? - Risk Management Studio
Organizations may be certified compliant with ISO/IEC 27001 by a number of accredited certification bodies worldwide. Certification against any of the recognized national variants of ISO/IEC 27001 (e.g. the Japanese version) by an accredited certification body is functionally equivalent to certification against ISO/IEC 27001 itself. Certification audits are usually conducted by ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditors.
In some countries, the bodies which verify conformity of management systems to specified standards are called "certification bodies", in others "registration bodies", "assessment and registration bodies", "certification/ registration bodies", and sometimes "registrars".
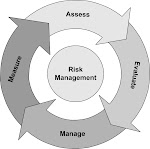
ISO/IEC 27001 certification usually involves a three-stage audit process:
Stage 1 is a "table top" review of the existence and completeness of key documentation such as the organization's security policy, Statement of Applicability (SoA) and Risk Treatment Plan (RTP).
Stage 2 is a detailed, in-depth audit involving testing the existence and effectiveness of the information security controls stated in the SoA and RTP, as well as their supporting documentation.
Stage 3 is a follow-up reassessment audit to confirm that a previously-certified organization remains in compliance with the standard. Certification maintenance involves periodic reviews and reassessments to confirm that the ISMS continues to operate as specified and intended.
Risk Management Studio is software that guides you through the three-stage audit process for ISO/IEC 27001 certification and makes it a much smoother and faster process.
Source
Hello Karma,
First of all, it is a pleasure to welcome you to the forum as probably our
first member from Bhutan. Welcome!
Without more specific information from you, it is difficult to answer your
question except in a rather general way but I hope the following suggestions
help for now.
1. ISO/IEC 27005 covers risk management, including risk assessment, in the
context of information security. It isn't a checklist but a more generic
description of the process of building your own approach to assessing and
managing information security risks.
2. ISO/IEC 27002 also mentions risk management and assessment, but is
mostly a menu of information security controls addressing a wide variety of
situations. It is a worthwhile model or template against which to review a
specific set of controls, and can be turned into a checklist provided it is
interpreted sensibly at 'run time'. I certainly use it in this manner, as a
reminder of the most important information security controls that I would
normally check for a client. The structure and detail in '27002 is very
helpful to structure and inform an audit report, for example.
3. There are various goodies in the free ISO27k Toolkit at:
www.iso27001security.com/html/
recommend a good look at:
www.iso27001security.com/
4. ISACA's COBIT is another way to structure a security audit, assessment
or review: see www.isaca.org/Knowledge-
If you need something more specific, please let us know. There are just
under 2,000 people on this forum with a wealth of experience to tap into.
Kind regards,
Gary
Gary Hinson
UPS: abbreviation or oxymoron?
www.NoticeBored.com Creative awareness materials
www.ISO27001security.com ISO/IEC 27000 standards
www.isect.com/html/















.jpg)





.jpg)

.jpg)









.jpg)

.jpg)














.jpg)


.jpg)


























































































































































































































.jpg)

.jpg)











.jpg)
















































.jpg)
















.jpg)












































































































































.jpg)

























March 30th, 2010 at 13:01