| 1 | Determine if any directives apply to your product. If more than one applies you will have to comply with all of them. |
| 2 | Determine the extent to which your product complies with the essential requirements for design and manufacturing in the applicable directive(s). |
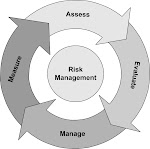
| 3 | Choose the conformity assessment procedure from the options (modules) called out by the directive for your product. There are several modules available for the Conformity Assessment Procedures as listed below: Module A: internal production control Module Aa: intervention of a Notified Body Module B: EC type-examination Module C: conformity to type Module D: production quality assurance Module E: product quality assurance Module F: product verification Module G: unit verification Module H: full quality assurance |
Options for products with minimal risk include self certification where the manufacturer prepares a Declaration of Conformity and affixes the CE Marking to their own product.
Many directives require products/systems with greater risks to be independently certified; this must be done by a "Notified Body". This is an organisation that has been nominated by a Member Government and has been notified by the European Commission. Notified bodies serve as independent test labs and perform the steps called out by directives. They must have the necessary qualifications to meet the testing requirements set forth in the directives. Notified bodies may be a private sector organization or a government agency. Manufacturers may choose a notified body in any member state of the European Union. Lists of notified bodies are published by the European Commission in the Official Journal of the European Communities.
Source















.jpg)





.jpg)

.jpg)









.jpg)

.jpg)














.jpg)


.jpg)


























































































































































































































.jpg)

.jpg)











.jpg)
















































.jpg)
















.jpg)












































































































































.jpg)

























No comments:
Post a Comment